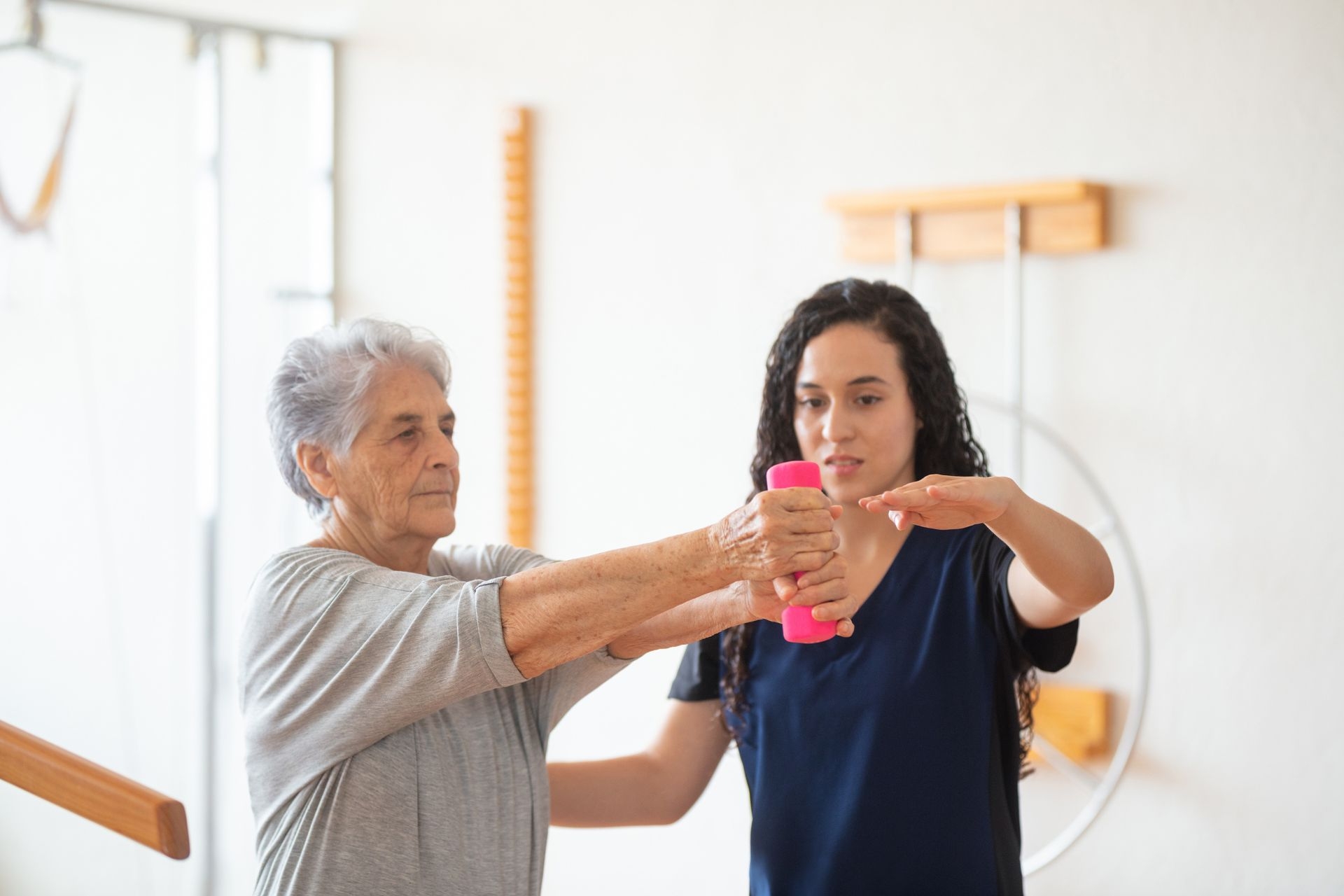


Postpartum abdominal separation, also known as diastasis recti, can be improved through specific exercises that target the core muscles. Neuro-IFRAH Approach Some effective exercises include pelvic tilts, heel slides, and abdominal compressions. These exercises help to strengthen the deep abdominal muscles and promote proper alignment of the abdominal wall. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a postpartum fitness specialist to ensure that you are performing the exercises correctly and safely.
The recovery time for postpartum pelvic floor muscles can vary from woman to woman. On average, it takes about six to eight weeks for the pelvic floor muscles to heal after childbirth. However, it is important to note that this timeline can be influenced by factors such as the type of delivery, the presence of any complications, and individual differences in healing. It is recommended to gradually reintroduce pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, after the initial healing period to help strengthen and restore the muscles.
Graston TechniquePostpartum back pain is a common concern for many women. Stretching exercises can help alleviate this discomfort by targeting the muscles that support the spine. Gentle stretches such as cat-cow pose, child's pose, and seated forward bends can help relieve tension in the back and promote flexibility. Additionally, exercises that strengthen the core and improve posture, such as bird dog and bridge exercises, can also be beneficial in reducing postpartum back pain.

Common symptoms of postpartum diastasis recti include a visible bulge or gap in the abdominal area, lower back pain, and a weakened core. Treatment for diastasis recti typically involves exercises that focus on strengthening the deep abdominal muscles and promoting proper alignment of the abdominal wall. Running Analysis These exercises may include pelvic tilts, heel slides, and abdominal compressions. In some cases, a physical therapist or postpartum fitness specialist may recommend the use of a support garment or brace to provide additional support to the abdominal muscles.
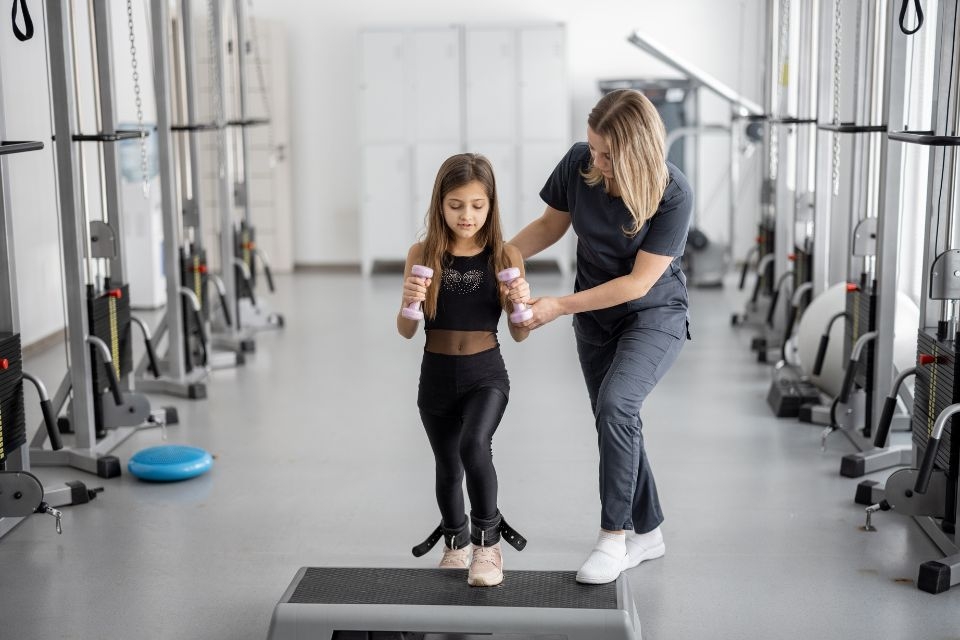
It is generally safe to start postpartum exercise immediately after giving birth, but it is important to listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise program. In the immediate postpartum period, gentle movements such as walking and gentle stretching can help promote circulation and aid in recovery. As your body heals, you can gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. It is important to start slowly and gradually progress to avoid overexertion and to allow your body to properly heal.
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles after childbirth is crucial for restoring their function and preventing issues such as urinary incontinence. Kegel exercises are a popular and effective way to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. To perform Kegels, simply contract and hold the muscles that you would use to stop the flow of urine. Hold the contraction for a few seconds, then release. Repeat this exercise several times throughout the day. Vestibular Testing Additionally, incorporating exercises that engage the core and glute muscles, such as squats and bridges, can also help strengthen the pelvic floor.
Women who have had a cesarean section should take certain precautions and modifications when engaging in postpartum exercise. It is important to wait until you have received clearance from your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program. Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) Initially, focus on gentle movements and avoid exercises that put strain on the abdominal muscles. As you progress, gradually incorporate exercises that strengthen the core and promote overall strength and flexibility. It is important to listen to your body and stop any exercise that causes pain or discomfort. Additionally, wearing a supportive abdominal binder or brace during exercise can provide added support to the incision site.

Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management and treatment of ankle impingement. By employing a variety of techniques and exercises, physical therapists aim to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and restore function to the affected ankle joint. They may utilize manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations to address any restrictions or tightness in the ankle joint and surrounding structures. Additionally, they may prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle, improve stability, and correct any imbalances or weaknesses that may be contributing to the impingement. These exercises may include ankle range of motion exercises, proprioceptive training, balance exercises, and strengthening exercises for the calf, foot, and ankle muscles. Physical therapists may also incorporate modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help reduce pain and inflammation in the ankle. Overall, physical therapy provides a comprehensive and individualized approach to managing ankle impingement, helping individuals regain optimal function and return to their daily activities.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of spinal stenosis. By employing a variety of techniques and exercises, physical therapists can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function in individuals with this condition. One of the primary goals of physical therapy is to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, which can help provide better support and stability to the affected area. Therapists may also use manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue massage, to reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, they may incorporate stretching exercises to increase flexibility and improve range of motion. By tailoring treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient, physical therapy can effectively manage spinal stenosis and improve quality of life.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis by providing targeted interventions to improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life. Through a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy, physical therapists aim to alleviate pain, increase range of motion, and strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joints. They also educate patients on proper body mechanics and joint protection techniques to minimize further damage. Additionally, physical therapists may recommend assistive devices, such as braces or orthotics, to provide support and stability. By tailoring treatment plans to individual needs, physical therapy helps individuals with osteoarthritis regain mobility, improve functional abilities, and manage their condition effectively.
Physical therapy is an effective treatment option for individuals with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). POTS is a condition characterized by an abnormal increase in heart rate upon standing, often accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue. Physical therapists utilize a variety of techniques to address the underlying causes of POTS and improve symptoms. These may include exercises to improve cardiovascular fitness, such as aerobic conditioning and interval training. Additionally, physical therapists may employ techniques to improve postural control and balance, such as balance training and proprioceptive exercises. They may also utilize manual therapy techniques to address any musculoskeletal imbalances or restrictions that may be contributing to symptoms. Overall, physical therapy aims to improve cardiovascular function, enhance postural stability, and alleviate symptoms associated with POTS, ultimately improving the individual's quality of life.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the rehabilitation of individuals with aortic dissection. Aortic dissection is a serious condition that involves a tear in the inner layer of the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The goal of physical therapy in aortic dissection rehabilitation is to improve overall cardiovascular fitness, enhance mobility, and promote functional independence. Physical therapists may utilize a variety of techniques, including therapeutic exercises, cardiovascular conditioning, and manual therapy, to address specific impairments and limitations caused by the condition. Additionally, they may provide education on lifestyle modifications, such as proper body mechanics and activity pacing, to prevent further complications and promote long-term health. By working closely with a physical therapist, individuals with aortic dissection can optimize their recovery and regain their quality of life.
The treatment approaches for Achilles tendinosis in physical therapy typically involve a combination of modalities and exercises. Modalities such as ultrasound, laser therapy, and electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area. Additionally, manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization may be employed to improve tissue mobility and reduce tension in the Achilles tendon. Strengthening exercises for the calf muscles and eccentric exercises specifically targeting the Achilles tendon are commonly prescribed to improve tendon strength and promote healing. Other interventions may include stretching exercises, gait analysis, and footwear modifications to address any underlying biomechanical issues that may be contributing to the condition. The treatment plan is usually tailored to the individual needs of the patient and may be adjusted as necessary throughout the rehabilitation process.