
The most common orthopedic conditions that require physical therapy include fractures, sprains, strains, tendonitis, bursitis, and joint replacements. Sports Medicine Fractures often require physical therapy to regain strength and mobility in the affected area. Sprains and strains, which are common injuries in sports, can benefit from physical therapy to reduce pain and inflammation and improve range of motion. Tendonitis and bursitis, which involve inflammation of tendons and bursae respectively, can be managed through physical therapy techniques such as stretching and strengthening exercises. Joint replacements, such as hip or knee replacements, often require physical therapy to help patients regain function and mobility in the replaced joint.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of orthopedic injuries by promoting healing, reducing pain, and restoring function. Physical therapists use various techniques such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities like heat or cold therapy to address the specific needs of each patient. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue mobilization, help improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tension. Therapeutic exercises, including stretching and strengthening exercises, help restore muscle strength and flexibility. Modalities like heat or cold therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation. By combining these approaches, physical therapy helps patients recover from orthopedic injuries and regain their independence.
Orthopedic physical therapy utilizes a range of treatment techniques to address different conditions and injuries. These techniques include manual therapy, which involves hands-on techniques to mobilize joints, manipulate soft tissues, and improve circulation. Therapeutic exercises are also commonly used, including stretching exercises to improve flexibility and strengthening exercises to build muscle strength. Other techniques may include electrical stimulation, ultrasound therapy, and hot or cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapists may also use assistive devices such as braces or crutches to support and protect injured areas during the healing process. The specific treatment techniques used will depend on the individual's condition and goals of therapy.
Post-Operative Care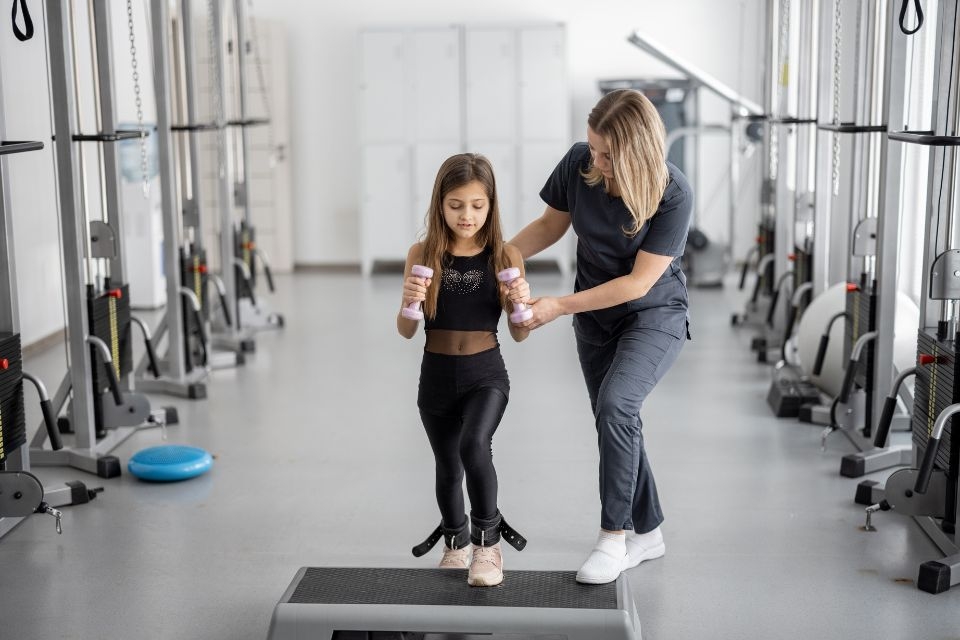
Yes, physical therapy can help in managing chronic orthopedic conditions. Chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic back pain can benefit from physical therapy interventions. Physical therapists can develop personalized treatment plans that focus on pain management, improving joint mobility, and enhancing overall function. Core Strengthening Through a combination of manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and education on self-management techniques, physical therapy can help individuals with chronic orthopedic conditions reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance their quality of life.
Exercise plays a crucial role in orthopedic physical therapy. It helps improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, which are essential for the rehabilitation of orthopedic injuries. Exercise can help strengthen muscles around the affected joint, providing stability and support. It also helps improve range of motion and flexibility, reducing the risk of further injury. Physical therapists prescribe specific exercises tailored to each individual's needs and goals. These exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and cardiovascular exercises. Regular exercise not only aids in the recovery process but also helps prevent future orthopedic injuries.

The recovery time from orthopedic injuries with the help of physical therapy can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the individual's overall health, and their adherence to the treatment plan. Tai Chi for Rehabilitation In general, physical therapy can significantly accelerate the recovery process. For minor injuries, such as sprains or strains, recovery may take a few weeks to a couple of months with consistent physical therapy sessions. More severe injuries, such as fractures or joint replacements, may require several months of physical therapy to regain full function and mobility. It is important to follow the guidance of the physical therapist and adhere to the prescribed exercises and treatment plan to achieve optimal recovery.
During orthopedic physical therapy, it is important to follow specific precautions and guidelines to prevent further injury. Physical therapists provide instructions on proper body mechanics and movement techniques to avoid strain or excessive stress on the injured area. Patients may be advised to avoid certain activities or movements that could worsen the condition. It is important to communicate any pain or discomfort experienced during therapy sessions to the physical therapist, as they can modify the treatment plan accordingly. Additionally, patients should adhere to any home exercise programs provided by the physical therapist and follow any recommendations for rest, icing, or elevation of the injured area. By following these precautions and guidelines, individuals can safely and effectively recover from orthopedic injuries with the help of physical therapy.
Injury Prevention
The treatment strategies for scoliosis in physical therapy typically involve a combination of exercises, manual therapy techniques, and bracing. Physical therapists may use specific exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve posture. These exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and stabilization exercises. Manual therapy techniques, such as spinal mobilization and soft tissue massage, may also be used to improve joint mobility and reduce pain. In some cases, a brace may be recommended to help correct the curvature of the spine. The type of brace and duration of wear will depend on the severity of the scoliosis. Physical therapists will also provide education and guidance on proper body mechanics and postural awareness to help manage symptoms and prevent further progression of the condition.
Yes, physical therapy can be an effective treatment for patellofemoral pain syndrome. Patellofemoral pain syndrome, also known as runner's knee, is a common condition characterized by pain around the kneecap. Physical therapy interventions for patellofemoral pain syndrome typically include a combination of exercises, manual therapy techniques, and education. These interventions aim to address the underlying causes of the pain, such as muscle imbalances, poor biomechanics, and overuse. Specific exercises may focus on strengthening the quadriceps, hip muscles, and core, as well as improving flexibility and balance. Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization, can help reduce pain and improve joint function. Additionally, education on proper body mechanics and activity modification can help prevent further aggravation of the condition. Overall, physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of patellofemoral pain syndrome, helping individuals reduce pain, improve function, and return to their desired activities.
Physical therapists play a crucial role in assisting individuals with tarsal tunnel syndrome by providing comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation. They employ a variety of techniques and modalities to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. Physical therapists may use manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization, and stretching exercises to address any restrictions or imbalances in the foot and ankle. They may also utilize therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the tarsal tunnel and improve overall stability. Additionally, physical therapists may incorporate modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and ice or heat therapy to further reduce pain and inflammation. Through a personalized treatment plan, physical therapists aim to restore function, improve quality of life, and prevent future complications for individuals with tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Postural restoration is a specialized approach to physical therapy that focuses on correcting imbalances in the body's posture and alignment. Unlike traditional physical therapy, which often treats specific injuries or conditions, postural restoration takes a holistic approach to address the underlying causes of pain and dysfunction. This approach recognizes that the body is a complex system of interconnected parts, and that imbalances in one area can affect the entire system. Postural restoration uses a variety of techniques, including manual therapy, exercises, and breathing techniques, to restore balance and alignment to the body. By addressing the root causes of pain and dysfunction, postural restoration aims to provide long-term relief and improve overall function and well-being.
Physical therapy is a highly effective treatment option for individuals recovering from a meniscus tear. By utilizing a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation, physical therapists can help patients regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected knee. The therapy sessions may include exercises that focus on improving balance, stability, and proprioception, as well as stretching and strengthening exercises for the surrounding muscles. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper body mechanics and techniques to prevent further injury. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process for individuals with a meniscus tear, helping them regain function and return to their normal activities.
Physical therapy can be a valuable component in the management of lymphedema. Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, typically in the arms or legs, due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Physical therapy interventions, such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, exercise, and education, can help reduce swelling, improve lymphatic flow, and enhance overall function and quality of life for individuals with lymphedema. By utilizing specialized techniques and modalities, physical therapists can assist in reducing edema, promoting tissue healing, and preventing complications associated with lymphedema. Additionally, physical therapists can provide guidance on self-care strategies, including skin care, exercise, and compression garment use, to help individuals manage their condition effectively. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of lymphedema, providing individuals with the tools and support they need to optimize their health and well-being.
Paraneoplastic pemphigus is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that is associated with an underlying malignancy. While physical therapy does not directly treat paraneoplastic pemphigus, it can play a supportive role in the rehabilitation process. Rehabilitation techniques for paraneoplastic pemphigus may focus on improving range of motion, strength, and functional mobility. Physical therapists may utilize exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy to help manage pain and inflammation. Additionally, they may provide education on proper body mechanics and postural awareness to prevent further complications. The goal of physical therapy in paraneoplastic pemphigus is to optimize the patient's physical function and quality of life while working in collaboration with the patient's medical team.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of Huntington's disease. By focusing on improving mobility, strength, balance, and coordination, physical therapy can help individuals with Huntington's disease maintain their independence and quality of life. Specific exercises and techniques, such as gait training, range of motion exercises, and balance training, can address the motor symptoms associated with the disease. Additionally, physical therapy can also provide education and support to both the individual with Huntington's disease and their caregivers, helping them understand the disease progression and providing strategies to manage symptoms effectively. Overall, physical therapy can be an integral part of a comprehensive treatment plan for individuals with Huntington's disease, promoting functional abilities and enhancing overall well-being.