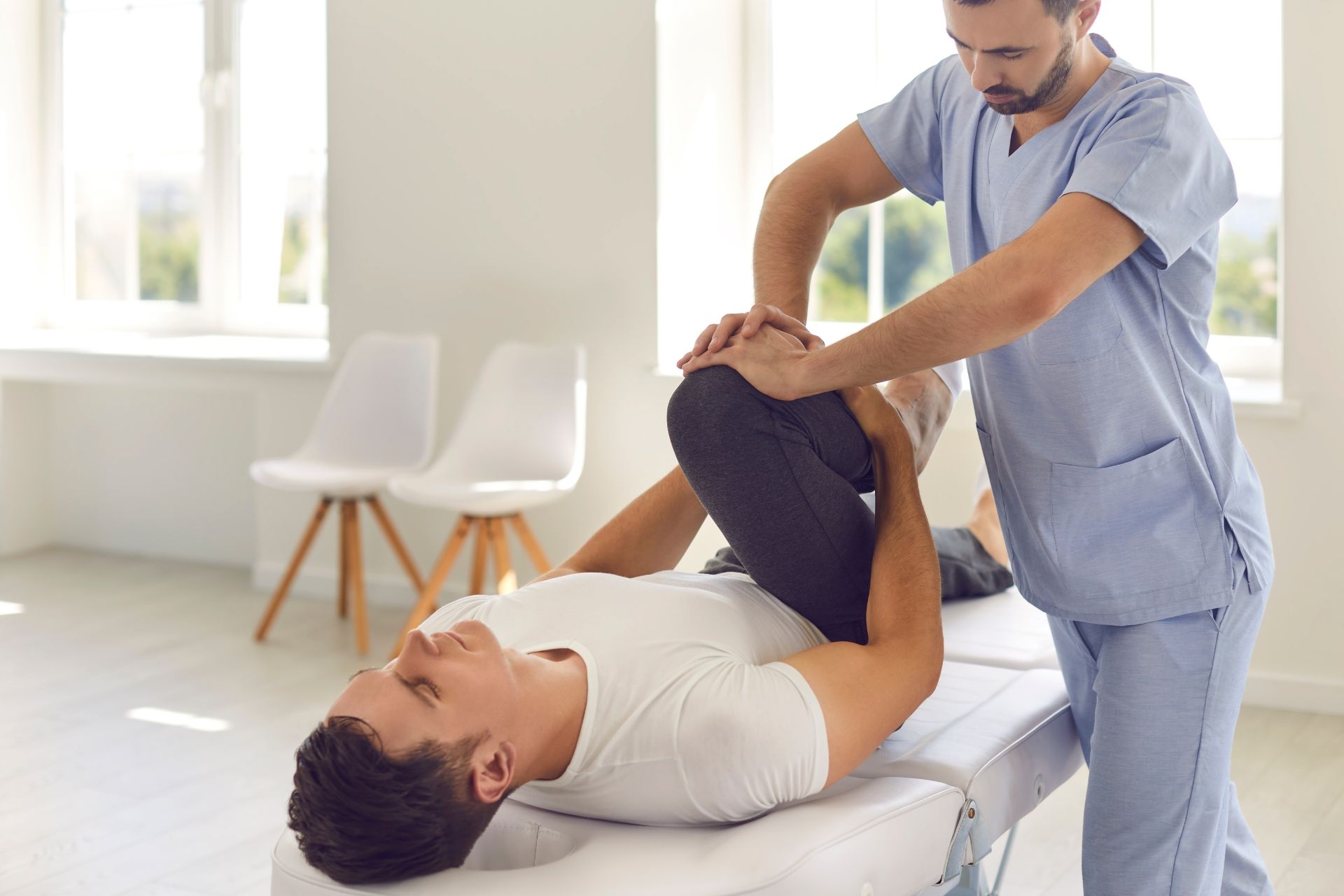

A Functional Capacity Evaluation (FCE) is an assessment conducted by occupational therapists to evaluate an individual's physical and cognitive abilities in relation to their capacity to perform work-related tasks. Cupping Therapy It is an important tool in occupational therapy as it helps determine an individual's functional limitations and abilities, which in turn informs the development of appropriate treatment plans and recommendations for work-related accommodations. By assessing an individual's functional capacity, occupational therapists can tailor interventions to improve their ability to perform daily activities and return to work successfully.
A Functional Capacity Evaluation typically involves several components to assess an individual's physical and cognitive abilities. These components may include a comprehensive medical history review, physical examinations, functional testing, and standardized assessments. The evaluation may also include observations of the individual's performance during simulated work tasks or activities of daily living. Occupational therapists may use various tools and equipment to measure an individual's strength, range of motion, endurance, coordination, and cognitive abilities. The evaluation process is usually conducted in a controlled environment, such as a clinic or rehabilitation center, to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Blood Flow Restriction TherapyThe main objectives of a Functional Capacity Evaluation are to determine an individual's functional limitations and abilities, assess their readiness to return to work, identify any barriers to work-related tasks, and develop appropriate treatment plans or recommendations for work-related accommodations. The evaluation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of an individual's physical and cognitive capabilities, which can guide the development of interventions to improve their functional capacity. Postural Correction By identifying an individual's strengths and limitations, occupational therapists can tailor their treatment plans to address specific areas of concern and help individuals regain their independence and productivity in the workplace.
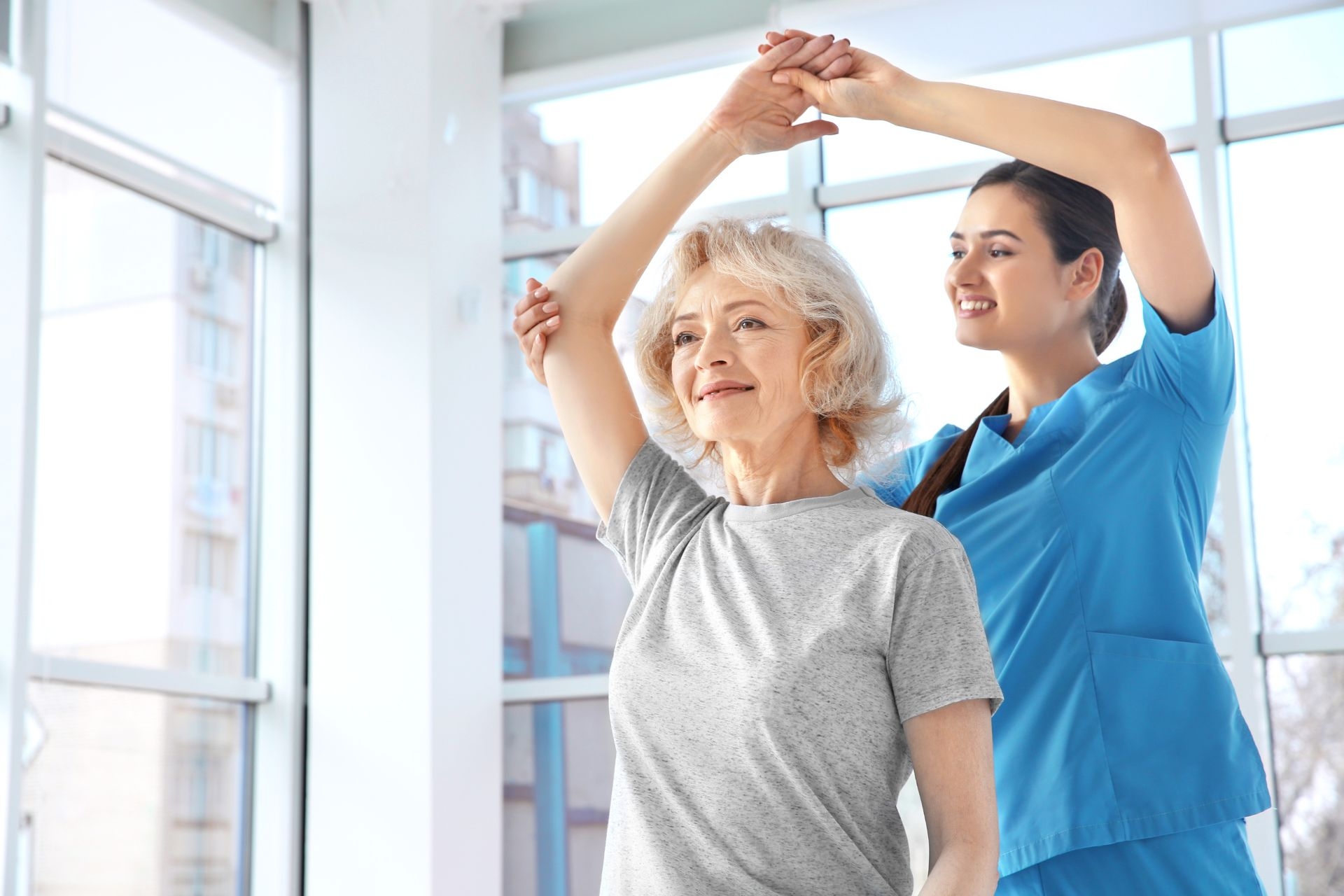

There are various types of assessments used in a Functional Capacity Evaluation. These assessments may include physical performance tests, such as lifting, carrying, pushing, and pulling tasks, to evaluate an individual's physical abilities. Cognitive assessments may also be conducted to assess an individual's attention, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. Additionally, functional tests may be used to evaluate an individual's ability to perform specific work-related tasks, such as typing, reaching, or operating machinery. Movement Therapy These assessments provide objective data on an individual's functional capacity and help guide the development of appropriate interventions and recommendations.
A Functional Capacity Evaluation plays a crucial role in determining an individual's ability to return to work or perform specific job tasks. Neurological Rehabilitation By assessing an individual's physical and cognitive abilities, occupational therapists can identify any functional limitations or barriers that may hinder their ability to perform work-related tasks. The evaluation provides objective data on an individual's functional capacity, which can be compared to the physical demands of their job. This comparison helps determine if an individual is capable of returning to their previous job or if modifications or accommodations are necessary. The evaluation also helps identify any areas of improvement or interventions that may be needed to enhance an individual's functional capacity for work.
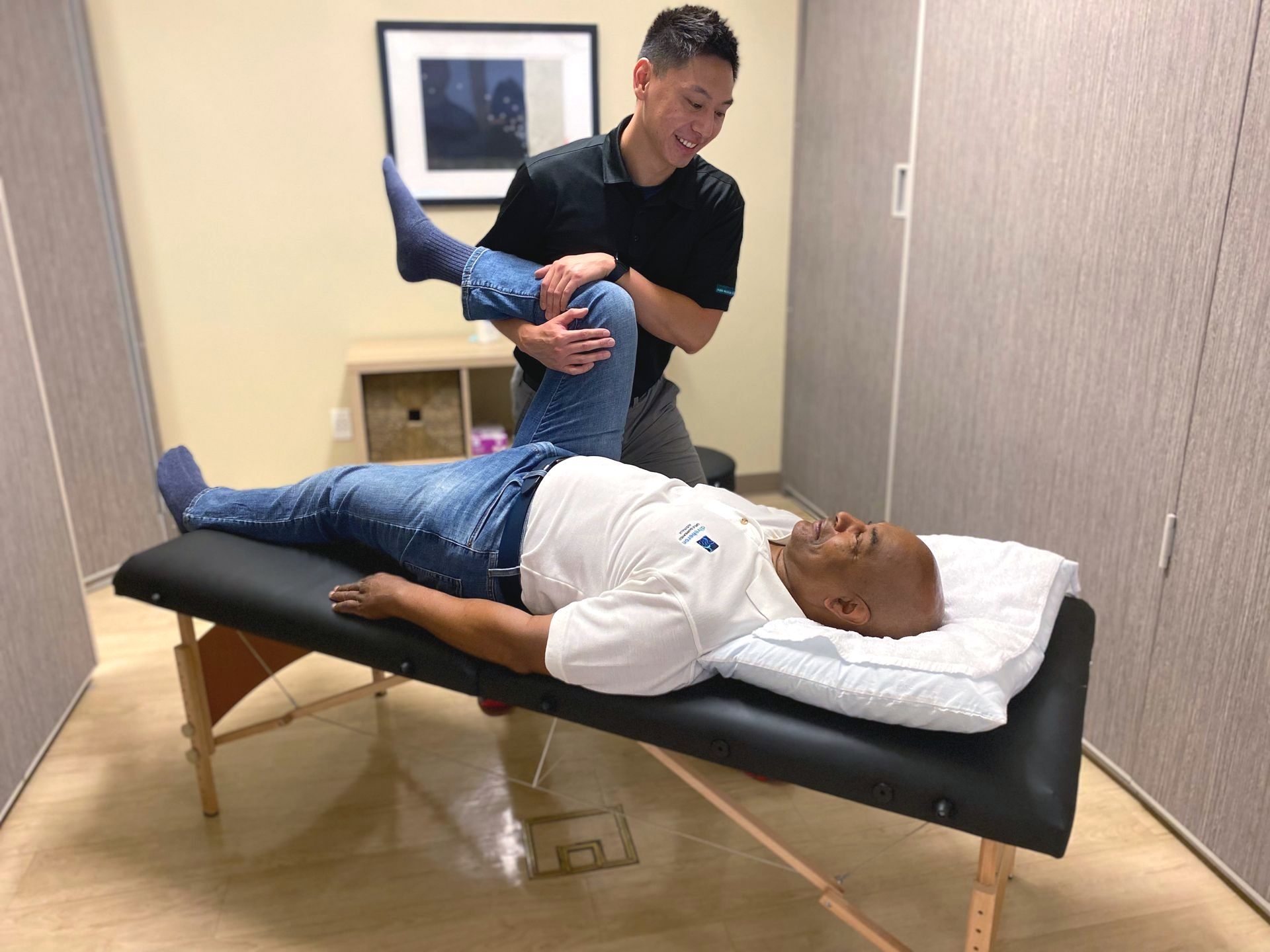
There are potential limitations and challenges associated with conducting a Functional Capacity Evaluation. One challenge is ensuring the evaluation accurately reflects an individual's true functional capacity, as the assessment is conducted in a controlled environment and may not fully replicate the demands of their specific job. Additionally, individual factors such as motivation, pain tolerance, and anxiety can influence the results of the evaluation. Occupational therapists must also consider cultural and contextual factors that may impact an individual's functional capacity. It is important for therapists to use a combination of objective assessments, clinical judgment, and client-centered approaches to ensure a comprehensive and accurate evaluation.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in addressing postpartum recovery by providing specialized treatment and exercises that target the specific needs of women after childbirth. These treatments focus on restoring pelvic floor strength, improving core stability, and addressing any musculoskeletal issues that may have arisen during pregnancy and delivery. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques, such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and biofeedback, to help women regain strength, flexibility, and function in their pelvic region. They also provide education on proper body mechanics and posture, as well as guidance on safe return to exercise and activities of daily living. By addressing the unique challenges faced by women during the postpartum period, physical therapy helps promote a faster and more complete recovery, allowing women to regain their pre-pregnancy level of function and quality of life.
Physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals suffering from metatarsalgia. Metatarsalgia is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot, often caused by excessive pressure or overuse. Physical therapy interventions such as stretching exercises, manual therapy techniques, and strengthening exercises can help alleviate pain, improve flexibility, and restore normal function in the affected area. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper footwear, gait training, and activity modification to prevent further aggravation of the condition. By addressing the underlying causes and providing targeted interventions, physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management and rehabilitation of individuals with metatarsalgia.
Physical therapists take a comprehensive and individualized approach to rehabilitation for bunions. They begin by conducting a thorough assessment of the patient's condition, including evaluating the severity of the bunion, assessing the range of motion and strength of the affected foot, and identifying any contributing factors such as muscle imbalances or faulty biomechanics. Based on this assessment, the physical therapist develops a personalized treatment plan that may include a combination of manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, to improve joint mobility and reduce pain. They may also prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the foot and ankle, improve balance and proprioception, and correct any muscle imbalances. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper footwear and foot care, as well as recommendations for orthotics or other assistive devices to support the foot and alleviate pressure on the bunion. Throughout the rehabilitation process, physical therapists closely monitor the patient's progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan to ensure optimal outcomes.
The treatment strategies for iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) in physical therapy typically involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and activity modification. Manual therapy techniques may include soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, and joint mobilization to address any muscle imbalances or restrictions in the IT band and surrounding structures. Therapeutic exercises often focus on strengthening the hip abductors and external rotators, as well as improving core stability and lower extremity alignment. Activity modification may involve temporarily reducing or modifying activities that aggravate the symptoms, such as running on uneven surfaces or excessive downhill running. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper running mechanics and footwear selection to prevent future episodes of ITBS.
The treatment approaches for Rett syndrome in physical therapy typically involve a multidisciplinary approach that focuses on improving motor skills, mobility, and functional abilities. Physical therapists may use a variety of techniques and interventions, such as therapeutic exercises, stretching, and range of motion exercises, to help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. They may also incorporate activities that promote balance and postural control, as well as assistive devices and adaptive equipment to enhance mobility and independence. Additionally, physical therapists may work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists and speech therapists, to address specific needs and challenges associated with Rett syndrome, such as hand function and communication skills. Overall, the goal of physical therapy for individuals with Rett syndrome is to optimize physical function and quality of life.