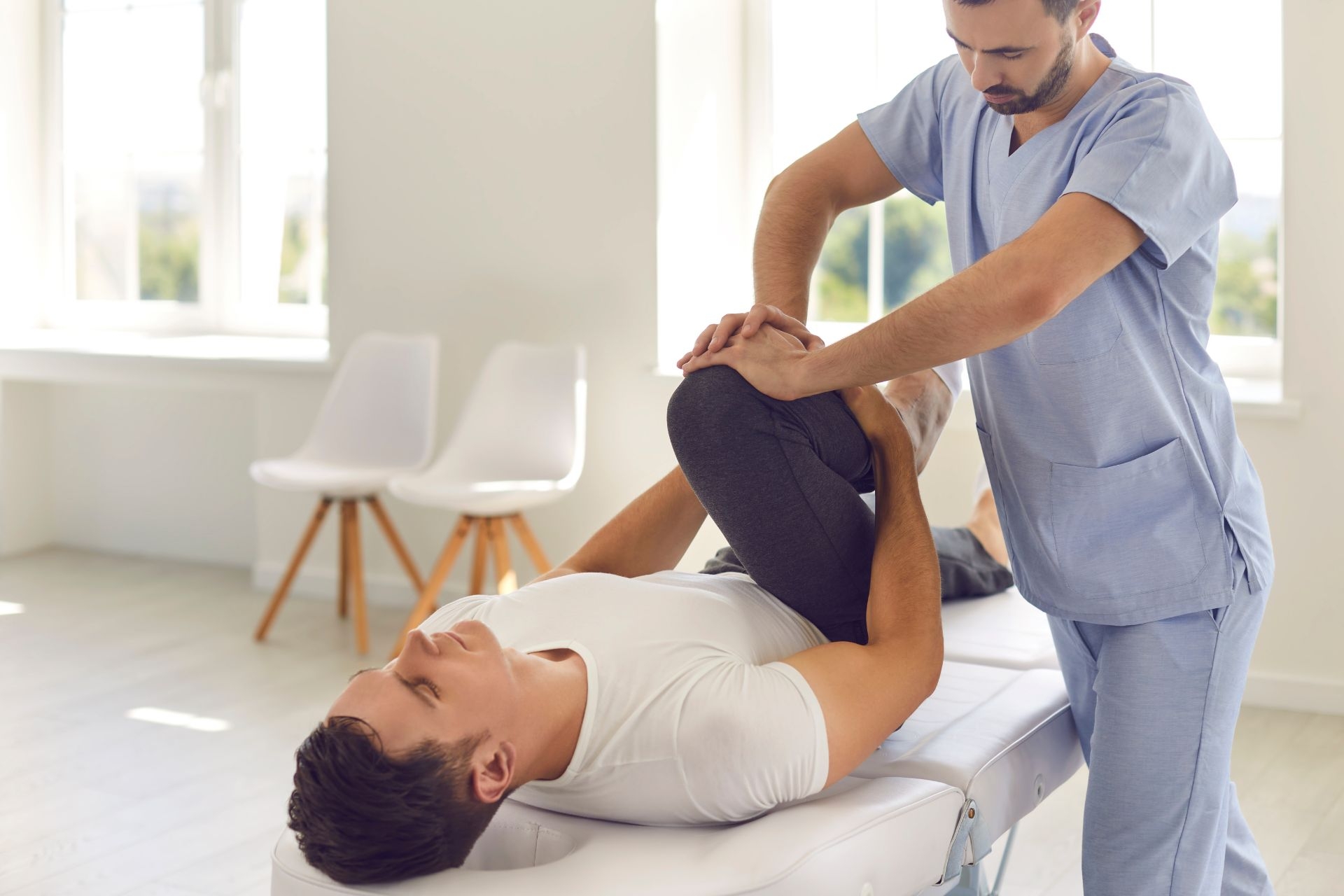

Instrument-assisted joint mobilization is a technique used in physical therapy to improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Muscle Energy Techniques It involves the use of specialized tools, such as metal or plastic instruments, to apply controlled pressure and movement to the affected joint. This differs from manual joint mobilization, which is performed by the therapist using their hands to manipulate the joint. The main difference between the two techniques is the use of instruments in instrument-assisted joint mobilization, which allows for more precise and targeted treatment.
There are several benefits of using instrument-assisted joint mobilization in physical therapy. Plyometric Training Firstly, it can help to break up scar tissue and adhesions that may have formed in the joint, which can improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Additionally, it can help to increase blood flow to the area, which can promote healing and reduce inflammation. Instrument-assisted joint mobilization can also help to improve joint range of motion and flexibility, allowing patients to regain functional movement and participate in activities they may have been unable to do before.
Instrument-assisted joint mobilization can be effectively used to treat a variety of conditions and injuries. It is commonly used in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, such as osteoarthritis, tendinitis, and frozen shoulder. It can also be beneficial for individuals recovering from joint surgeries, such as knee or hip replacements. Additionally, it can be used to address soft tissue restrictions and joint dysfunctions in athletes or individuals with repetitive strain injuries.
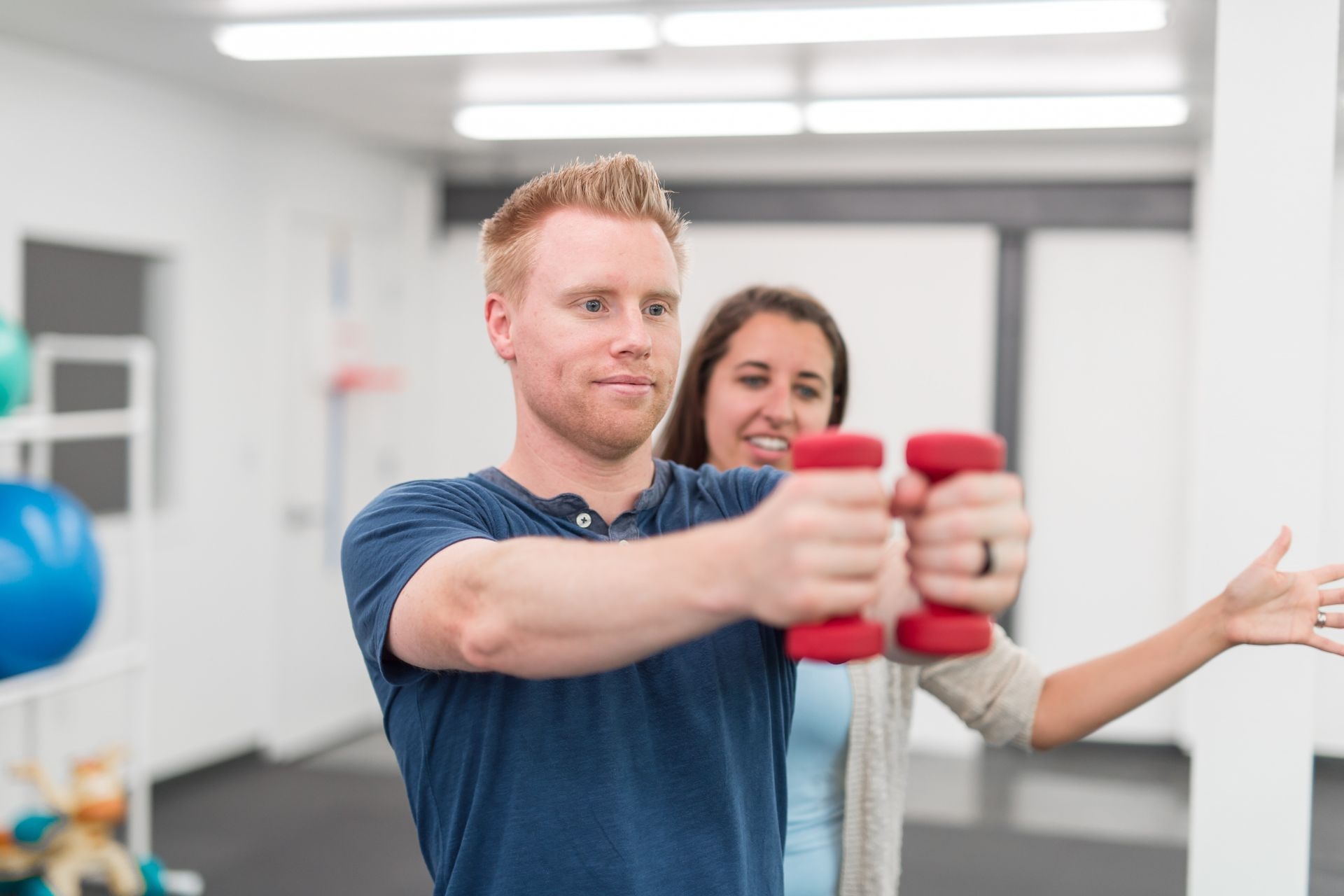

Instrument-assisted joint mobilization helps improve joint range of motion and flexibility by targeting the underlying structures of the joint. The controlled pressure and movement applied by the instruments help to break up scar tissue and adhesions, which can restrict joint movement. This allows for increased joint mobility and flexibility. Additionally, the increased blood flow to the area can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing, further improving joint range of motion.
RehabilitationWhile instrument-assisted joint mobilization is generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and side effects to be aware of. These can include temporary soreness or discomfort in the treated area, bruising, and skin irritation. Postpartum Rehabilitation In rare cases, there may be a risk of injury if the technique is not performed correctly or if the patient has certain underlying conditions. It is important for the therapist to assess the patient's individual needs and limitations before using instrument-assisted joint mobilization.
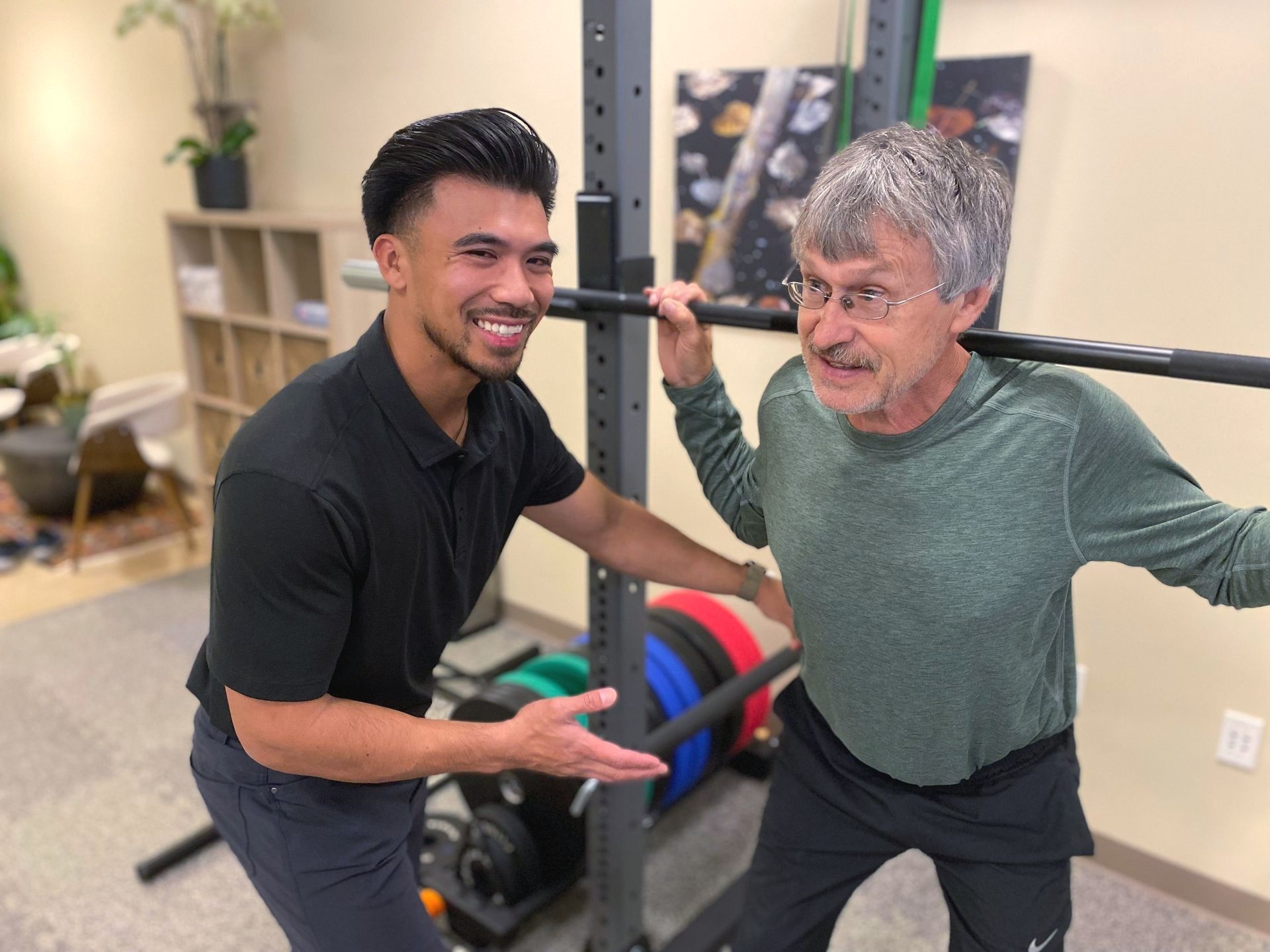

Yes, instrument-assisted joint mobilization can be used in conjunction with other treatment modalities in physical therapy. It is often combined with exercise therapy, where specific exercises are prescribed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint and improve overall function. Additionally, it can be used alongside manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization or soft tissue mobilization, to provide a comprehensive treatment approach. The combination of these modalities can help to optimize outcomes and improve overall patient function.
The duration of a typical instrument-assisted joint mobilization session can vary depending on the individual needs of the patient and the specific joint being treated. Generally, a session can last anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes. The number of sessions required to see results will also vary depending on the severity of the condition or injury, as well as the individual's response to treatment. Neurological Rehabilitation In some cases, significant improvement may be seen after just a few sessions, while others may require ongoing treatment over a longer period of time. The therapist will work closely with the patient to develop a personalized treatment plan and monitor progress throughout the course of therapy.

Physical therapists play a crucial role in addressing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) by implementing a comprehensive treatment plan that focuses on improving mobility, strength, and overall quality of life for individuals with this condition. They utilize a variety of therapeutic techniques, such as manual therapy, stretching exercises, and balance training, to address the specific needs of each patient. Physical therapists also provide education on proper body mechanics and assistive devices to help individuals with CMT maintain optimal function and prevent further complications. Additionally, they may collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as orthotists and neurologists, to ensure a multidisciplinary approach to managing CMT. By tailoring their interventions to the unique challenges posed by CMT, physical therapists help individuals with this condition maximize their functional abilities and enhance their overall well-being.
Physical therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals suffering from shin splints. Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are a common overuse injury that causes pain along the shin bone. Physical therapy interventions such as therapeutic exercises, stretching, and manual therapy techniques can help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Specific exercises targeting the lower leg muscles, such as calf raises and ankle dorsiflexion exercises, can improve strength and flexibility, which can prevent further injury and promote proper biomechanics. Additionally, physical therapists can provide education on proper footwear, running techniques, and training modifications to prevent future occurrences of shin splints. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management and rehabilitation of shin splints, helping individuals regain function and return to their normal activities.
Functional dry needling is a technique used in physical therapy that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific trigger points in the muscles to relieve pain and improve function. The key principles of functional dry needling include identifying and targeting the trigger points, using a sterile technique to ensure safety and prevent infection, and applying the needles with precision and accuracy to achieve optimal results. Additionally, the therapist must have a thorough understanding of anatomy and neurophysiology to effectively locate and treat the trigger points. The treatment should be tailored to the individual patient's needs and goals, and the therapist should continuously assess and reassess the patient's response to the treatment to make any necessary adjustments. Overall, functional dry needling aims to restore normal muscle function, reduce pain, and improve overall physical performance.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing Osgood-Schlatter disease. Osgood-Schlatter disease is a condition that affects the growth plate in the knee, causing pain and inflammation. Physical therapy aims to reduce pain, improve strength and flexibility, and promote healing. Therapists may use a variety of techniques, such as stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like ice or heat therapy. They may also provide education on proper body mechanics and activity modification to prevent further injury. By addressing the underlying causes and symptoms of Osgood-Schlatter disease, physical therapy can help individuals manage their condition and return to their normal activities with reduced pain and improved function.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) by addressing the various physical impairments and functional limitations associated with the disease. Through a comprehensive evaluation, physical therapists develop individualized treatment plans that focus on maintaining and improving mobility, strength, and overall physical function. They may employ a range of techniques, including therapeutic exercises, stretching, range of motion exercises, and balance training, to help manage muscle weakness, spasticity, and loss of coordination. Additionally, physical therapists may utilize assistive devices and adaptive equipment to enhance independence and optimize daily activities. By working closely with patients, physical therapists aim to maximize their quality of life and promote overall well-being.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing post-polio syndrome by addressing the specific needs and challenges faced by individuals with this condition. Through a comprehensive evaluation, physical therapists can assess the patient's functional abilities, muscle strength, range of motion, and balance. Based on the assessment findings, they develop personalized treatment plans that may include exercises to improve muscle strength and endurance, stretching to maintain or improve flexibility, and balance training to reduce the risk of falls. Additionally, physical therapists may use modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, or ultrasound to alleviate pain and promote tissue healing. They also educate patients on energy conservation techniques and assistive devices to optimize their daily activities and minimize fatigue. By providing targeted interventions, physical therapy helps individuals with post-polio syndrome enhance their overall quality of life and maintain their independence.
Physical therapists take a comprehensive and individualized approach to rehabilitation following hip arthroscopy. They begin by assessing the patient's specific condition, including the extent of the hip joint damage, any associated muscle imbalances, and the patient's overall functional goals. Based on this assessment, the physical therapist develops a tailored treatment plan that may include a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or ice therapy. The therapist focuses on improving range of motion, strength, and stability of the hip joint, while also addressing any compensatory movement patterns or muscle imbalances that may have developed. They may also incorporate functional training exercises to help the patient regain their ability to perform daily activities and return to their desired level of physical activity. Throughout the rehabilitation process, the physical therapist closely monitors the patient's progress and adjusts the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal outcomes.