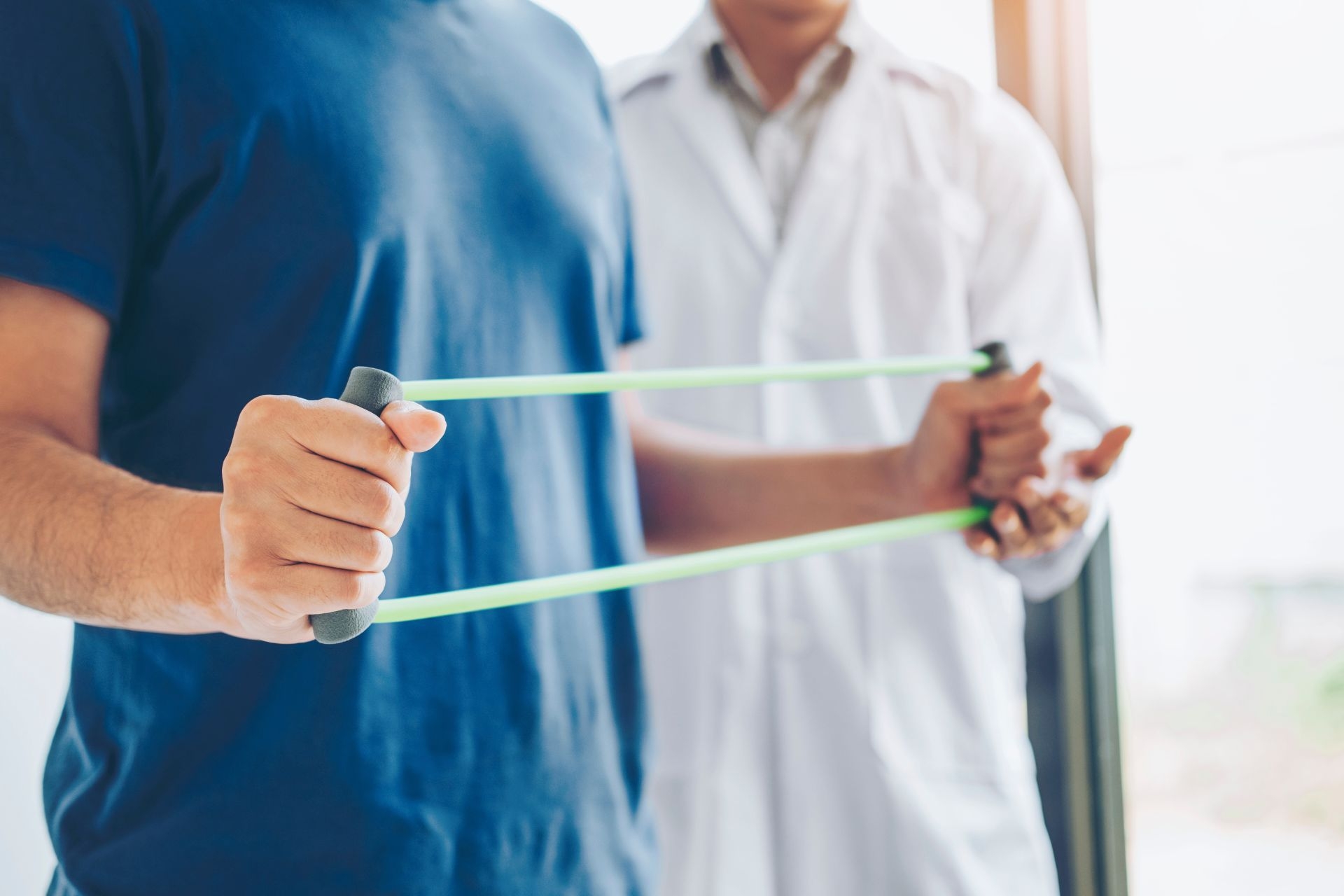


Hand therapy is a specialized form of rehabilitation that focuses on treating conditions and injuries affecting the hand, wrist, and forearm. It differs from regular physical therapy in that it specifically targets the intricate structures and functions of the hand. Functional Rehabilitation Hand therapists are trained to assess and treat a wide range of hand-related issues, including fractures, tendon injuries, nerve damage, and repetitive strain injuries. They use a combination of manual techniques, exercises, and modalities to improve hand function and reduce pain. Hand therapy aims to restore optimal hand function, promote independence, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals with hand injuries or conditions.
Hand therapy can help treat a variety of common conditions affecting the hand. Some of these include carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger finger, tennis elbow, De Quervain's tenosynovitis, arthritis, and Dupuytren's contracture. Hand therapists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans based on their specific condition and individual needs. They may use techniques such as splinting, therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like heat or cold therapy to alleviate pain, improve range of motion, and restore hand function.
Sports PerformanceHand therapy plays a crucial role in post-operative rehabilitation for hand surgeries. After a hand surgery, such as tendon repair or joint replacement, hand therapy helps promote healing, reduce swelling, and prevent complications. Neurological Rehabilitation Hand therapists work closely with the surgeon to develop a comprehensive rehabilitation plan tailored to the individual's needs. They may use techniques such as scar management, gentle mobilization exercises, and progressive strengthening exercises to restore hand function and maximize recovery. Hand therapy also focuses on educating patients about proper post-operative care and self-management techniques to ensure a successful rehabilitation outcome.

Yes, hand therapy can be highly beneficial for individuals with arthritis in their hands. Arthritis can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the hands, making it challenging to perform daily activities. Hand therapists can help manage arthritis symptoms by providing pain relief techniques, such as joint mobilizations and modalities like heat or cold therapy. They also teach patients exercises to improve joint flexibility, strengthen the surrounding muscles, and enhance hand function. Additionally, hand therapists may recommend the use of assistive devices or splints to support the joints and reduce stress on the affected areas.
Hand therapy utilizes various techniques to improve range of motion and strength in the hand. Aquatic Plyometrics These techniques may include therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, splinting, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy. Therapeutic exercises are designed to target specific muscles and joints in the hand, promoting flexibility, strength, and coordination. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, help improve joint mobility and reduce pain. Splinting is often used to support and protect injured or surgically repaired structures, allowing for proper healing and functional recovery. Modalities like heat or cold therapy can help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling, facilitating the healing process.
In addition to attending hand therapy sessions, there are exercises and activities that can be done at home to complement the treatment. Hand therapists often provide patients with home exercise programs tailored to their specific needs and goals. These exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and coordination exercises that can be performed using simple household items or specialized hand therapy tools. Manual Therapy It is important to follow the therapist's instructions and guidelines to ensure proper technique and avoid any potential harm. Consistency and adherence to the home exercise program are key to achieving optimal results.
The duration of hand therapy and the frequency of sessions can vary depending on the individual's condition and treatment goals. Typically, hand therapy may last for several weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the injury or condition. Initially, sessions may be scheduled more frequently, such as two to three times per week, to address acute symptoms and promote early recovery. As the individual progresses, the frequency of sessions may decrease to once a week or every other week. The duration and frequency of hand therapy sessions are determined by the hand therapist in collaboration with the patient, taking into consideration factors such as progress, response to treatment, and individual needs.

The treatment strategies for iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) in physical therapy typically involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and activity modification. Manual therapy techniques may include soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, and joint mobilization to address any muscle imbalances or restrictions in the IT band and surrounding structures. Therapeutic exercises often focus on strengthening the hip abductors and external rotators, as well as improving core stability and lower extremity alignment. Activity modification may involve temporarily reducing or modifying activities that aggravate the symptoms, such as running on uneven surfaces or excessive downhill running. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on proper running mechanics and footwear selection to prevent future episodes of ITBS.
The treatment approaches for Rett syndrome in physical therapy typically involve a multidisciplinary approach that focuses on improving motor skills, mobility, and functional abilities. Physical therapists may use a variety of techniques and interventions, such as therapeutic exercises, stretching, and range of motion exercises, to help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination. They may also incorporate activities that promote balance and postural control, as well as assistive devices and adaptive equipment to enhance mobility and independence. Additionally, physical therapists may work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists and speech therapists, to address specific needs and challenges associated with Rett syndrome, such as hand function and communication skills. Overall, the goal of physical therapy for individuals with Rett syndrome is to optimize physical function and quality of life.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of adhesive capsulitis, commonly known as frozen shoulder. The primary goal of physical therapy is to improve the range of motion and reduce pain in the affected shoulder joint. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques and modalities to achieve these goals, including manual therapy, stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and joint mobilization. They may also incorporate heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to help alleviate pain and inflammation. Additionally, physical therapists provide education and guidance on proper posture, body mechanics, and home exercises to promote long-term recovery and prevent future episodes of frozen shoulder. By addressing the underlying causes and symptoms of adhesive capsulitis, physical therapy can significantly improve the functional abilities and quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Aquatic physical therapy offers a range of benefits for individuals seeking rehabilitation or pain management. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact on joints, making it an ideal environment for those with conditions such as arthritis or joint injuries. The resistance provided by water also helps to strengthen muscles and improve overall flexibility. Additionally, the hydrostatic pressure of water can reduce swelling and improve circulation, aiding in the healing process. Aquatic therapy can also enhance balance and coordination, as individuals must adapt to the water's resistance and instability. Overall, aquatic physical therapy provides a low-impact, effective, and enjoyable way to improve physical function and quality of life.
Physical therapy is an integral part of the comprehensive treatment approach for fibrous dysplasia. The primary goal of physical therapy is to improve the patient's functional abilities and quality of life. Physical therapists utilize a variety of techniques and modalities to address the specific needs of individuals with fibrous dysplasia. These may include therapeutic exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, as well as manual therapy techniques to reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, physical therapists may employ modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound to further enhance the effectiveness of treatment. By tailoring the treatment plan to the individual's unique needs, physical therapy can help manage symptoms, improve physical function, and promote overall well-being in individuals with fibrous dysplasia.
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for individuals with chronic ankle instability. By focusing on strengthening the muscles surrounding the ankle joint, improving balance and proprioception, and addressing any underlying biomechanical issues, physical therapy aims to enhance stability and reduce the risk of recurrent ankle sprains. Therapeutic exercises, such as ankle strengthening exercises, balance training, and proprioceptive training, can help improve muscle strength, joint stability, and overall ankle function. Additionally, manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, may be used to address any joint restrictions or muscle imbalances that contribute to ankle instability. Overall, physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of chronic ankle instability, helping individuals regain stability, improve function, and prevent future injuries.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of individuals with an Achilles tendon rupture. The primary goal of physical therapy is to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected tendon and surrounding muscles. Therapists use a variety of techniques and exercises to achieve this, including stretching, strengthening exercises, manual therapy, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation. These interventions help to improve blood flow, reduce pain and inflammation, and promote tissue healing. Additionally, physical therapy focuses on improving balance, coordination, and proprioception to prevent future injuries. By addressing the specific needs of each individual, physical therapy helps to optimize recovery and enhance overall quality of life.