
Common symptoms of lymphedema include swelling in the affected limb, a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the limb, decreased flexibility, and recurring infections. Other symptoms may include aching or discomfort in the limb, thickening or hardening of the skin, and restricted range of motion. It is important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition.
Pain Neuroscience EducationLymphedema is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. The healthcare provider will ask about any previous surgeries or treatments that may have affected the lymphatic system. They will also assess the affected limb for signs of swelling, skin changes, and other symptoms. Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Imaging tests such as lymphoscintigraphy or MRI may be used to visualize the lymphatic system and confirm the diagnosis.
Lymphedema is classified into four stages based on the severity of the condition. In stage 0, there may be no visible swelling, but the lymphatic system is not functioning properly. Stage 1 is characterized by mild swelling that reduces with elevation. In stage 2, the swelling becomes more persistent and does not reduce with elevation. In the final stage, stage 3, the swelling becomes more severe and can lead to significant changes in the skin and tissues.

Treatment options for lymphedema aim to reduce swelling, manage symptoms, and improve overall quality of life. This may include manual lymphatic drainage, a specialized massage technique that helps move lymph fluid. Feldenkrais Method Compression therapy, such as wearing compression garments or bandages, can also help reduce swelling. Exercise programs, including specific exercises to promote lymphatic flow, may be recommended. In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered.
While lymphedema cannot always be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. It is important to avoid injury or trauma to the affected limb, as this can increase the risk of developing lymphedema. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good skin hygiene, and avoiding tight clothing or jewelry that restricts lymphatic flow can also help reduce the risk. It is important to follow any recommendations or precautions provided by healthcare professionals.

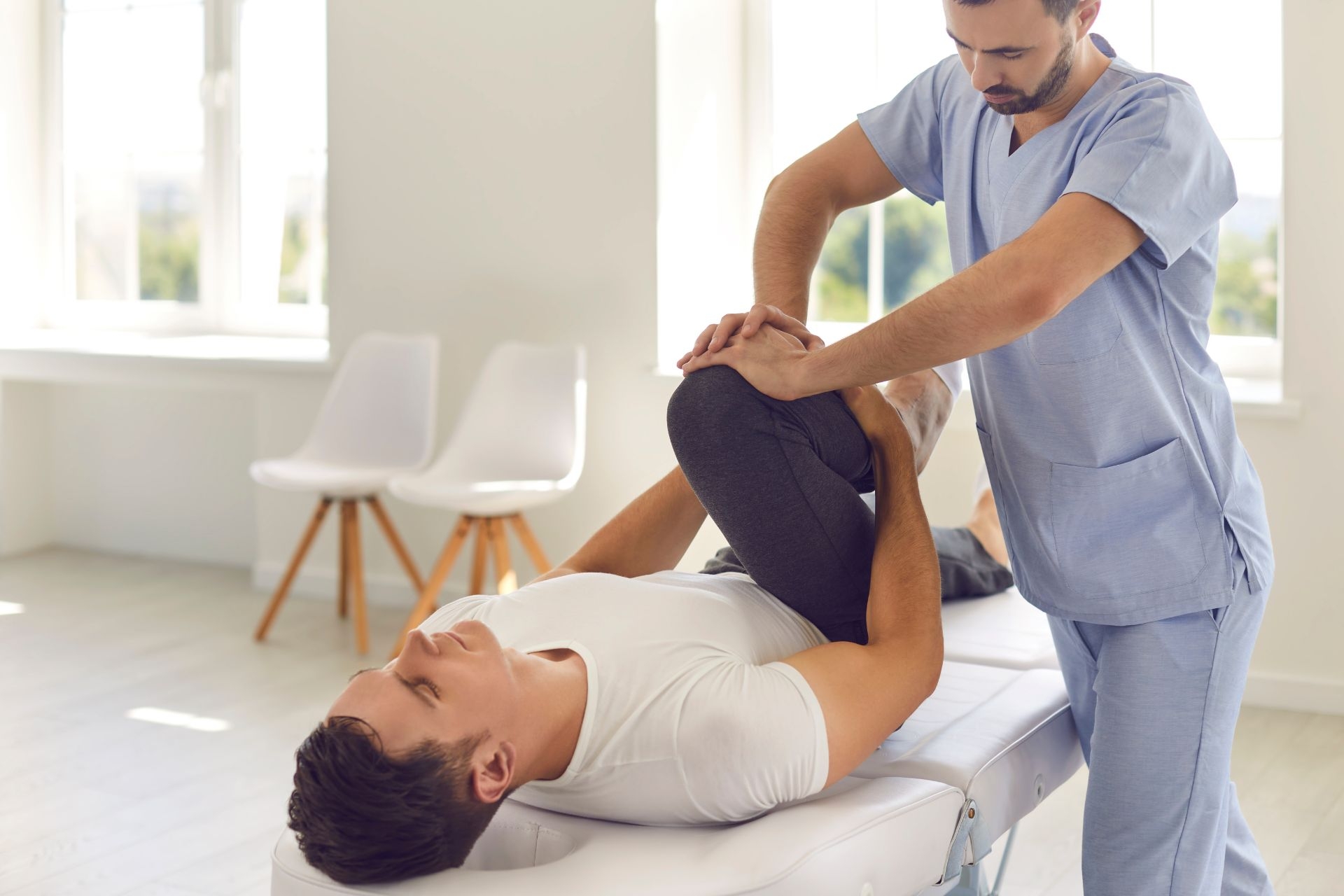
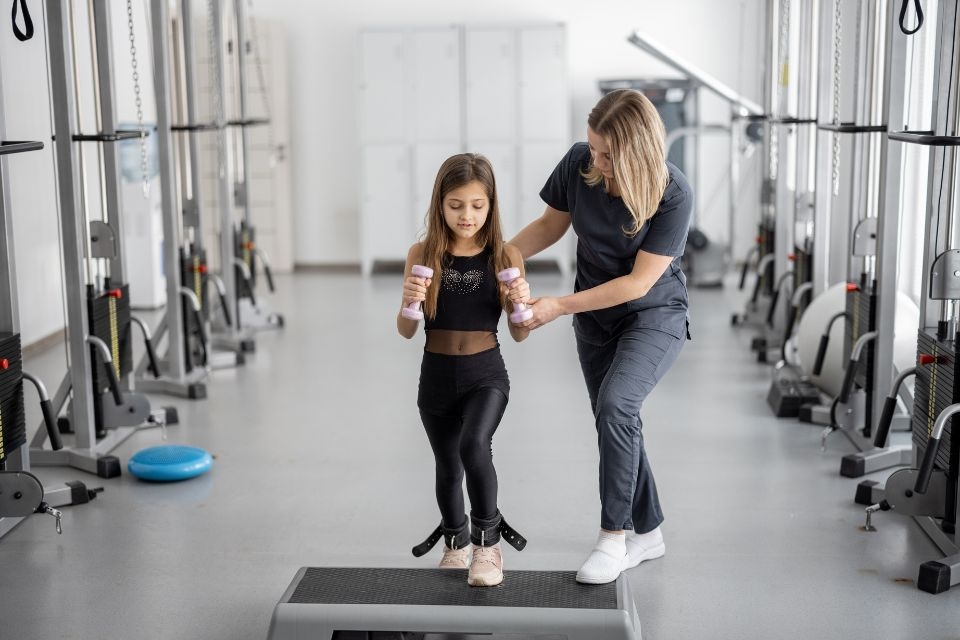
There are specific exercises and activities that can help manage lymphedema. These exercises, known as lymphatic exercises or lymphatic drainage exercises, aim to stimulate the flow of lymph fluid and reduce swelling. Tendinopathy Rehabilitation They may include gentle stretching, deep breathing exercises, and specific movements that target the affected limb. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified lymphedema therapist before starting any exercise program to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Untreated lymphedema can lead to various complications. Chronic swelling can cause changes in the skin, such as thickening, hardening, or ulceration. Recurring infections, such as cellulitis, can also occur. Over time, untreated lymphedema can lead to decreased mobility and function in the affected limb. It can also have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, causing emotional distress and affecting daily activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent or minimize these complications.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of hip labral tears. The primary goal of physical therapy is to reduce pain, improve hip joint stability, and restore normal function. Physical therapists use a combination of manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, to address any joint or muscle imbalances that may be contributing to the tear. They also prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, including the glutes, hip flexors, and core muscles. These exercises help to improve hip stability and reduce stress on the labrum. Additionally, physical therapists may use modalities such as heat or ice therapy to manage pain and inflammation. Through a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan, physical therapy can effectively manage hip labral tears and help patients regain their mobility and quality of life.
Piriformis syndrome is a condition that causes pain and discomfort in the buttocks and can be effectively treated through physical therapy. Physical therapists employ a variety of treatment approaches to address this condition. These may include manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization to reduce muscle tension and improve joint mobility. Therapeutic exercises are also commonly prescribed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the piriformis and improve overall stability. Additionally, stretching exercises are utilized to increase flexibility and alleviate tightness in the piriformis muscle. Modalities such as heat or ice therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Education on proper body mechanics and posture is often provided to prevent future episodes of piriformis syndrome. Overall, physical therapy offers a comprehensive and individualized approach to treating piriformis syndrome, aiming to reduce pain, improve function, and enhance the patient's quality of life.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing femoral acetabular impingement (FAI). FAI is a condition characterized by abnormal contact between the femoral head and the acetabulum, leading to pain and limited range of motion in the hip joint. Physical therapy aims to address these symptoms and improve functional outcomes through a variety of interventions. These may include therapeutic exercises to strengthen the hip muscles, improve joint stability, and correct any imbalances or compensatory movements. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, can also be used to reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and restore normal movement patterns. Additionally, physical therapists may provide education on activity modification, ergonomics, and self-management strategies to help individuals with FAI better manage their condition and prevent further complications. By addressing the underlying impairments and promoting optimal movement patterns, physical therapy can significantly contribute to the management of FAI and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for individuals suffering from jumper's knee, also known as patellar tendinitis. By utilizing a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation, physical therapists can help reduce pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint. Additionally, they may provide education on proper biomechanics and training modifications to prevent further injury. The goal of physical therapy is to promote healing, restore function, and enable individuals to return to their normal activities.
Physical therapists use a variety of techniques to treat pelvic floor dysfunction. These may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, which help to strengthen and relax the muscles of the pelvic floor. They may also use biofeedback, which involves using sensors to provide visual or auditory feedback on muscle activity, helping patients to better understand and control their pelvic floor muscles. Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and myofascial release, may be used to address any muscle tightness or trigger points in the pelvic floor. Additionally, therapists may provide education on bladder and bowel habits, posture, and body mechanics to help manage symptoms and prevent further dysfunction.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing carpal tunnel syndrome by providing non-invasive treatment options that aim to alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent further progression of the condition. Through a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and ergonomic modifications, physical therapists can help individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected hand and wrist. These exercises may include wrist stretches, nerve gliding exercises, and strengthening exercises for the surrounding muscles. Additionally, physical therapists may educate patients on proper body mechanics and ergonomics to reduce strain on the wrist and prevent exacerbation of symptoms. By addressing the underlying causes and providing tailored interventions, physical therapy can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of chondromalacia patellae. The primary goal of physical therapy is to alleviate pain, improve knee function, and restore the strength and flexibility of the surrounding muscles. Therapists employ a variety of techniques, including therapeutic exercises, manual therapy, and modalities such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation. Therapeutic exercises focus on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles, as well as improving the stability and alignment of the knee joint. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue mobilization, help reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, modalities like ultrasound and electrical stimulation can aid in pain management and promote tissue healing. Physical therapy also includes education on proper body mechanics and activity modification to prevent further aggravation of the condition. Overall, physical therapy provides a comprehensive approach to address the specific needs of individuals with chondromalacia patellae, helping them regain optimal function and quality of life.
Physical therapists play a crucial role in addressing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) by implementing a comprehensive treatment plan that focuses on improving mobility, strength, and overall quality of life for individuals with this condition. They utilize a variety of therapeutic techniques, such as manual therapy, stretching exercises, and balance training, to address the specific needs of each patient. Physical therapists also provide education on proper body mechanics and assistive devices to help individuals with CMT maintain optimal function and prevent further complications. Additionally, they may collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as orthotists and neurologists, to ensure a multidisciplinary approach to managing CMT. By tailoring their interventions to the unique challenges posed by CMT, physical therapists help individuals with this condition maximize their functional abilities and enhance their overall well-being.