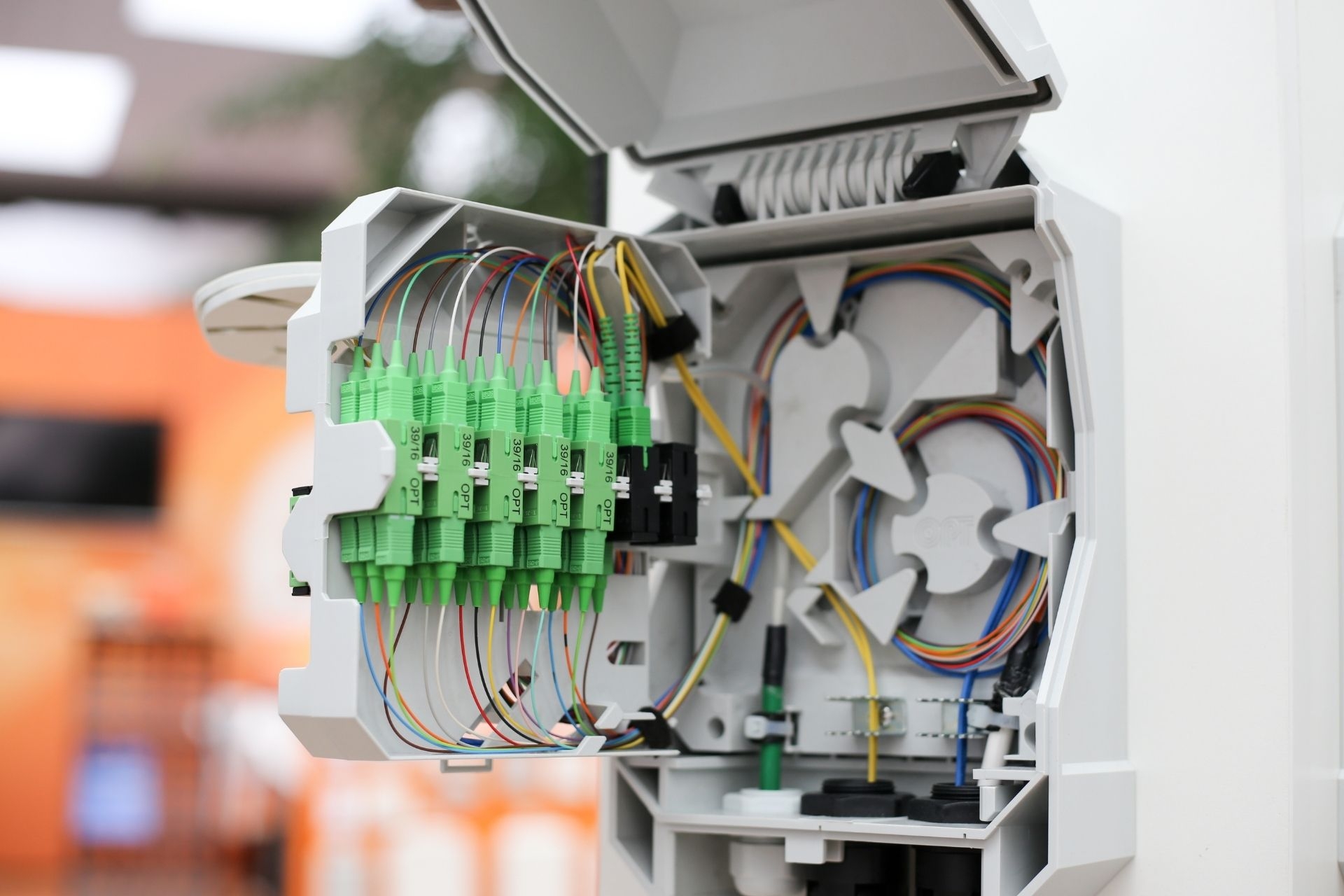
Deploying fiber optic internet in older MDUs presents several challenges due to the outdated infrastructure and construction of these buildings. One major challenge is the need for extensive retrofitting to accommodate the installation of fiber optic cables, as older MDUs may not have the necessary ductwork or pathways for the cables. Additionally, the layout of older MDUs can be complex, with multiple units and floors, making it difficult to run cables efficiently and effectively. Another challenge is gaining access to individual units for installation, as residents may be resistant to allowing technicians into their homes. Furthermore, the cost of upgrading an older MDU to support fiber optic internet can be prohibitive, as it may require significant structural changes and equipment upgrades. Overall, deploying fiber optic internet in older MDUs requires careful planning, coordination, and investment to overcome these challenges and provide residents with high-speed, reliable internet access.