Bfr Training for Skonny - BFR Training
Home
When Did Blood Flow Restriction Training Start
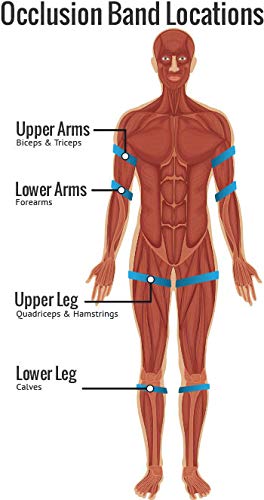
It can be applied to either the upper or lower limb. The cuff is then pumped up to a specific pressure with the objective of getting partial arterial and complete venous occlusion. what is bfr training. The patient is then asked to perform resistance workouts at a low strength of 20-30% of 1 repetition max (1RM), with high repetitions per set (15-30) and brief rest periods in between sets (30 seconds) Understanding the Physiology of Muscle Hypertrophy. Muscle hypertrophy is the increase in size of the muscle in addition to an increase of the protein content within the fibers.
Myostatin controls and inhibits cell growth in muscle tissue. It requires to be basically closed down for muscle hypertrophy to happen. b strong blood flow restriction. Resistance training results in the compression of capillary within the muscles being trained. This triggers an hypoxic environment due to a reduction in oxygen delivery to the muscle.
( 1) Low intensity BFR (LI-BFR) leads to an increase in the water content of the muscle cells (cell swelling). It likewise speeds up the recruitment of fast-twitch muscle fibers - does blood flow restriction training work. It is likewise hypothesized that as soon as the cuff is gotten rid of a hyperemia (excess of blood in the blood vessels) will form and this will cause additional cell swelling.
A large cuff is preferred in the right application of BFR. 10-12cm cuffs are typically utilized. A broad cuff of 15cm might be best to allow for even limitation. Modern cuffs are formed to fit the natural contour of the arm or thigh with a proximal to distal narrowing. There are also particular upper and lower limb cuffs that permit much better fitment.
The narrower cuffs are generally elastic and the larger nylon. With flexible cuffs there is an initial pressure even prior to the cuff is inflated and this results in a various capability to restrict blood flow as compared to nylon cuffs. Flexible cuffs have actually been shown to provide a substantially greater arterial occlusion pressure instead of nylon cuffs - blood flow restriction training research.
g. 180 mm, Hg; a pressure relative to the patient's systolic blood pressure, for e. g. 1. 2- or 1. 5-fold greater than systolic blood pressure; a pressure relative to the patient's thigh area. It is the best to utilize a pressure particular to each private patient, since various pressures occlude the quantity of blood flow for all people under the very same conditions.
Why Does Blood Flow Restriction Training Increase Heart Rate
The cuff is pumped up to a particular pressure where the arterial blood flow is entirely occluded. This called limb occlusion pressure (LOP) or arterial occlusion pressure (AOP). The cuff pressure is then computed as a portion of the LOP, typically in between 40%-80%. Using this technique is more effective as it ensures patients are working out at the appropriate pressure for them and the kind of cuff being utilized.
BFR-RE is typically a single joint exercise modality for strength training. Muscle hypertrophy can be observed during BFR-RE within a 3 week period however a lot of studies promote for longer training durations of more than 3 weeks. A load of 20-40% 1RM has actually been shown to produce consistent muscle adjustments for BFR-RE.
A systematic evaluation carried out by da Cunha Nascimento et al in 2019 took a look at the long and short term impacts on blood hemostasis (the balance between fibrinolysis and coagulation). It concluded that more research study requires to be conducted in the field before definitive standards can be provided. In this evaluation, they raised concerns about the following Unfavorable impacts were not constantly reported The level of prior training of subjects was not indicated which makes a significant distinction in physiological action Pressures used in research studies were very variable with various techniques of occlusion as well as requirements of occlusion Most studies were performed on a short-term basis and long term actions were not determined The studies focused on healthy topics and exempt with threat for thromboembolic disorders, impaired fibrinolysis, diabetes and obesity Their final conclusion on the safety of BFR was as such: In basic, it is well developed that unaccustomed exercise leads to muscle damage and delayed onset muscle pain (DOMS), especially if the workout includes a a great deal of eccentric actions. blood flow restriction cuffs.
As your body is recovery after surgical treatment, you might not be able to position high tensions on a muscle or ligament. Low load workouts might be needed, and blood circulation restriction training permits optimum strength gains with minimal, and safe, loads. Performing BFR Training Prior to beginning blood flow restriction training, or any exercise program, you should inspect in with your doctor to guarantee that exercise is safe for your condition (what is blood flow restriction training).
Release the contraction. Repeat slowly for 15 to 20 repetitions. Your physiotherapist might have you rest for 30 seconds and then repeat another set. Blood flow restriction training is expected to be low strength however high repetition, so it is typical to perform 2 to 3 sets of 15 to 20 representatives throughout each session.
Who Should Not Do BFR Training? Individuals with particular conditions ought to not engage in BFR training, as injury to the venous or arterial system may take place. Contraindications to BFR training may consist of: Prior to carrying out any workout, it is important to talk with your doctor and physiotherapist to make sure that exercise is ideal for you.
When Do You Take Off During Workout Blood Flow Restriction Training Bodybuilding
Over the last number of years, blood flow restriction training has received a lot of favorable attention as an outcome of the fantastic increases to size & strength it provides. However lots of people are still in the dark about how BFR training works. Here are 5 crucial tips you need to know when beginning BFR training.
There are a variety of different suggestions of what to utilize floating around the web; from knee wraps to over-sized rubber bands (blood flow restriction training for chest). However, to guarantee as accurate a pressure as possible when performing practical BFR training, we suggest purpose created options like our Bf, R Pro ARMS & Bf, R Pro LEGS straps.
On the other hand, some studies suggest to increase efficiency of your fast-twitch fibres (those for explosive power and strength) you should raise around 40% of your 1RM. Change Your Reps and Rest Durations Whilst you are going to be lowering the strength of weight you're lifting; you're going to be upping the intensity and volume of your workout.
For that reason, it is necessary that you adjust your recovery appropriately but compared to heavy lifting then there is less muscle damage when doing low load BFR training. Studies have actually revealed that no boosts in muscle damage continue longer than 24 hours after a BFR exercise implying it is safe to be performed every other day at many; however the very best gains in muscle size and strength have been found carrying out 2-3 sessions of BFR each week. Do be mindful, nevertheless, if you are simply beginning blood circulation limitation training or are unaccustomed to such high-repetition sets, you may need slightly longer to recuperate from such metabolically demanding training.
005) was observed only in the HIIT group. Both, GH and IGF-1 increased significantly immediately after the interventions, however without differences in between groups (no interaction effect). La increased throughout the intervention in a similar manner among both groups. Conclusions The combined intervention efficiently enhances the optimum power in context of endurance capacity.
However, the improved HIF-1 in the HIIT+BFR as compared to the HIIT recommends that the combined intervention might have a superior physiological stimulus. Based upon the presented theoretical background and the insights of the examination by Taylor, et al. , the purpose of this research study was to examine the results of a HIIT in mix with BFR (using KAATSU-cuffs) in contrast to a sole HIIT on physical efficiency.
How To Use Blood Flow Restriction Training
It is to be assumed that this intervention results in higher metabolic stress, which could catalyze adaption procedures in this context. To clarify the level of metabolic stress, the accumulation of blood lactate concentrations (La) during the intervention along with intense and basal modifications of the GH and IGF-1 have been determined (what is bfr training).
Study style The groups BFR+HIIT and HIIT performed a HIIT-intervention for four weeks, 3 times per week (Monday, Wednesday, Friday). Instantly prior to each HIIT-intervention, four sets of deep squats without extra load were performed by both groups. The BFR+HIIT group conducted the deep squats under BFR conditions. Within one week prior to (pre) and after (post) of the four-week intervention, the endurance capability was checked using a spiroergometry on a bicycle-ergometer.
The GH and IGF-1 were analysed immediately before and after the very first (T1, T2) and last (T3, T4) intervention to measure intense (T1 to T2 and T3 to T4) and basal (T1 to T3) changes. During the 6th intervention, the La were measured instantly prior to (pre) and after the BFR/squat (post BFR/squat) and after the HIIT (post HIIT).
This was performed on bicycle-ergometers (Kardiomed, Bike, Proxomed, Germany) and included 3 periods each lasting 4 minutes with a resting duration of one minute. The periods were performed with an intensity which was gotten used to the 2nd ventilatory threshold plus 5 percent (BFR+HIIT HR: 168 14 min-1 ; HIIT HR: 163 15 min-1 , with heart rate (HR) as the control specification (measured by the heart rate display FT7, Polar, Finland). This strength was selected since of the requirement that a HIIT should be performed at an intensity greater than the anaerobic threshold
For the pre-post contrast, the primary values of the height of the three CMJ were computed. The 1RM was figured out using the several repeating maximum test as explained by Reynolds, et al. The test was evaluated with the exercise dynamic leg press. Diagnostics of metabolic stress/growth elements Blood samples were collected by a medical doctor at those time points (T1, T2, T3, T4) from a shallow lower arm vein under tension conditions.
How Does Blood Flow Restriction Training Work
The blood samples were examined in a local medical laboratory. La was measured on the ear lobe of the individuals to the time points as pointed out in the study design. The samples were evaluated with the measuring device Super GL3 by HITADO (Germany; determining error < 1. 5% according to the maker's details).
For typically distributed data, the interaction result between the groups over the intervention time was talked to a two-way ANOVA with repeated steps (elements: time x group). Afterwards, differences in between measurement time points within a group (time result) and differences in between groups throughout a measurement time point (group effect) were evaluated with a dependent and independent t-test.
For that reason, the groups can be thought about uniform at the beginning of the intervention. Table 1: Mean values (basic discrepancy) of criteria of endurance and strength efficiency collected in the pre- and post-test in the BFR+HIIT group and HIIT group. View Table 1 After the 4 weeks of intervention, we determined a considerable increase in the optimum power in both groups with the boost in the BFR+HIIT group being around twice as high as in the HIIT group (see interaction result in Table 1).
But in the BFR+HIIT group, the boost in power during the VT1 was much higher than in the HIIT (see Table 1). These outcomes did not end up being statistically substantial but for the BFR+HIIT group, a propensity (0. 100 > p > 0. 050) was observed. The enhancements can be thought about practically relevant.
While the BFR+HIIT group had the ability to improve their power with constant HR (referring to the VT2 + 5%, see techniques) to + 8. 5% (1. to 2. week, p < 0. 001), + 8. 9% (2. to 3. week, p < 0. 001) and + 4 (blood flow restriction therapy). 0% (3. to 4.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5609669/
RS
SSL Active
What does blood flow restriction training do?
https://www.menshealth.com/fitness/a19534758/blood-flow-restriction-to-build-muscle/
SSL Active
What does BFR stand for in exercise?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6530612/
SSL Active
Does BFR training hurt?
https://www.sportsinjurybulletin.com/blood-flow-restriction-training-feel-the-pressure/
SSL Active
How often should I do BFR training?
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Blood_Flow_Restriction_Training
SSL Active
Does BFR training increase size?
https://www.forbes.com/sites/leebelltech/2019/03/30/smart-cuffs-how-blood-flow-restriction-training-is-the-next-big-fitness-trend/
SSL Active
Does BFR training increase strength?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6683630/
SSL Active
Are BFR bands dangerous?
BFR works through the partial occlusion of blood flow. According to multiple research studies, WIDER CUFFS DECREASE THE PRESSURE NEEDED TO RESTRICT BLOOD FLOW. This means that the small cuffs sold by many “BFR” manufacturers increase the risk of soft tissue damage.
https://thebarbellphysio.com/blood-flow-restriction-training-safe/
SSL Active
Who benefits from BFR training?
https://www.issaonline.com/blog/index.cfm/2020/blood-flow-restriction-training-what-trainers-need-to-know
SSL Active
What is the ideal BFR?
https://precisionhealthclinics.com.au/bfr-what-the-heck-is-it/
SSL Active
What are the benefits of BFR bands?
https://bstrong.training/blogs/articles/blood-flow-restriction-training-benefits
SSL Active
Do BFR bands really work?
https://www.onnit.com/academy/is-it-legit-occlusion-training-for-muscle-growth/
SSL Active
How does BFR build muscle?
Elastic BFR bands partially restrict the venous blood (oxygen deficient blood flowing from the limbs back to the heart) return. This makes the muscles work even harder to pump the blood back to the heart!Nov 13, 2020
https://www.athletico.com/2020/11/13/how-does-blood-flow-restriction-work/
SSL Active
How long can you keep BFR bands on?
https://www.bfrbands.com/faqs/
SSL Active
Can I do occlusion training everyday?
https://www.bfrbands.com/is-it-bad-to-do-the-same-exercise-every-day/
SSL Active
Does BFR work for chest?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20618358/
SSL Active
Where do you put your BFR band for your butt?
https://recoverfun.com/blogs/blood-flow-restriction-training/how-to-use-bfr-training-to-grow-your-arms-legs-and-booty
SSL Active
How do you program BFR training?
- The generally prescribed protocol is as follows: ...
- Set 1: 30 reps / Rest: 30-60 seconds.
- Set 2: 15 reps / Rest: 30-60 seconds.
- Set 3: 15 reps / Rest: 30-60 seconds.
- Set 4: 15 reps / Rest: 30-60 seconds. ...
- Barbell Bench Press 80-85% 1RM.
https://drjohnrusin.com/blood-flow-restriction-scientifically-advancing-muscular-strength-hypertrophy/
SSL Active
How tight should occlusion bands be?
https://www.bfrbands.com/tips-for-using-occlusion-training-wraps-effectively/
SSL Active
Does blood flow help muscle growth?
https://www.phd.com/perform-smart/the-importance-of-a-muscle-pump-for-increased-muscle-growth/
SSL Active
Does BFR increase HGH?
https://www.precisionpt.org/post/blood-flow-restriction-training-deserving-the-hype
SSL Active
How can I get huge muscles?
- Eat Breakfast to help build Muscle Mass. ...
- Eat every three hours. ...
- Eat Protein with Each Meal to Boost Your Muscle Mass. ...
- Eat fruit and vegetables with each meal. ...
- Eat carbs only after your workout. ...
- Eat healthy fats. ...
- Drink water to help you build Muscle Mass. ...
- Eat Whole Foods 90% of The Time.
https://www.everyoneactive.com/content-hub/gym/eight-tips-help-build-muscle-mass/
SSL Active
Can you use BFR bands while running?
https://pure-physio.com/endurance-bfr-training/
SSL Active
Can BFR training cause blood clots?
Research from surgical tourniquet tells us that complete vascular occlusion can cause the formation of a thrombus (blood clot). The incidence rate of suffering a venous thrombosis during BFR training is 0.06%, and this number is lower than the general population figure.
https://sujibfr.com/blogs/blog/is-blood-flow-restriction-training-safe
SSL Active
What are the best BFR bands?
- BFR Bands. Occlusion Training Bands. ...
- Superpump! Kaatsu-inspired Training Straps. ...
- Ronin Wraps. BFR Occlusion Bands (4 pack) ...
- Beast Pump. Occlusion Bands (4 pack) ...
- Lifting Lab. Ultimate Arm Builder.
https://bestreviews.com/best-occlusion-training-bands
SSL Active
Does BFR increase vascularity?
BFRT increases vascularity and allows you to build more strength from lighter loads. This allows you to do more repetitions. You may only need to use weights that are 20 percent of your normal weight.Sep 13, 2019
https://www.healthline.com/health/veiny-arms
SSL Active
001) as well as general to + 23. 7% (1. to 4. week, p < 0. 001), the enhancement of the power in the HIIT group was only + 5. 3% (1. to 2. week, p = 0. 049), + 5 (bfr training chest). 2% (2. to 3. week, p = 0. 023) and + 3.
<<< Next
Additional Information
Low Intensity Resistance Training With Blood Flow Restriction Brings Almost the Same Results - BFR Training
Blood Flow Restriction Training Bad for Bicep Tear? - BFR Training
Bfr Training for Skonny - BFR Training
Leave a Comment:
Blog Search
Popular Blog Categories
- blood flow restriction training
- bfr training
- blood flow restriction bands
- blood flow restriction therapy
- blood flow restriction training physical therapy
- blood flow restriction physical therapy
- blood flow restriction cuffs
- blood flow restriction training for chest
- what is blood flow restriction training
- what is bfr training